- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Technical Insights
- >
- Magnesium vs. Aluminum HPDC: The 7 Core Differences from Material to Process
Magnesium vs. Aluminum HPDC: The 7 Core Differences from Material to Process
As the two primary lightweight metals in modern industry, both magnesium and aluminum alloys play a crucial role in high-pressure die casting (HPDC). While their processing workflows may appear similar, their vast differences in physical and chemical properties dictate fundamentally different approaches to everything from equipment selection and process parameters to die design.
As experts deeply rooted in the casting industry, we are here to provide an in-depth analysis of the seven core differences between these two alloys in HPDC.
1. Material Properties & Molten Metal Protection
Melting Point: Magnesium alloys have a significantly lower melting point (approx. 430-630°C) compared to aluminum alloys (approx. 580-670°C).
Melt Protection: Magnesium is extremely reactive and will readily ignite at high temperatures. Therefore, its melting and holding processes must be protected by a cover gas like SF₆. In contrast, aluminum quickly forms a dense, stable alumina (Al₂O₃) layer on its surface, which provides natural protection, generally eliminating the need for a special cover gas.
2. Fluidity & Process Parameters
Fluidity: Magnesium alloys exhibit superior fluidity, allowing them to fill thin-walled and complex cavities more effectively.
Injection Pressure: Thanks to its excellent fluidity, magnesium HPDC requires lower injection pressures (40-100 MPa) than aluminum (80-120 MPa), which can contribute to longer die life.
Filling Speed: Magnesium's high thermal conductivity causes it to solidify rapidly. Consequently, it requires extremely high gate velocities (up to 100 m/s) to prevent defects like cold shuts.
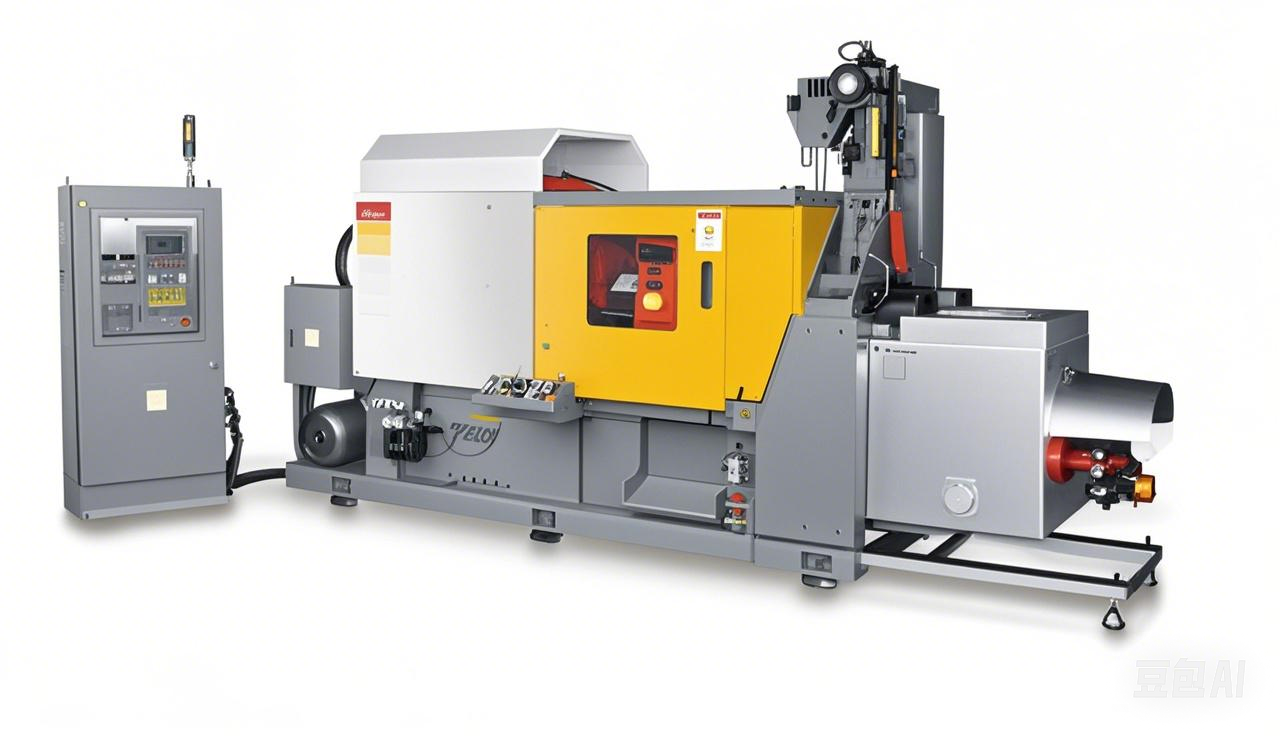

3. The Critical Difference in Equipment Selection
This is one of the most practical distinctions. Because magnesium is far less aggressive in attacking iron components (like the gooseneck and plunger) than aluminum is, and due to its lower melting point:
Small to medium-sized magnesium parts are often produced using highly efficient hot-chamber die casting machines.
Aluminum parts and larger magnesium parts universally require the use of cold-chamber die casting machines.
4. Die Design & Cooling
Die Temperature: The operating temperature for magnesium dies (150-250°C) is lower than that for aluminum (200-300°C).
Cooling System: Magnesium's low latent heat of fusion and fast solidification demand a highly efficient die cooling system (often using thermal oil for temperature control) to rapidly extract heat and shorten cycle times.
5. Corrosion Resistance & Surface Treatment
Magnesium has a very low standard electrode potential, making it far less chemically stable than aluminum. As a result, magnesium die-cast parts almost always require a surface treatment—such as passivation, e-coating, or painting—to meet corrosion resistance requirements. Aluminum, in most environments, has good natural corrosion resistance due to its self-passivating oxide layer.
6. Safety & Environmental Concerns
The magnesium production process requires strict fire and explosion prevention measures (magnesium powder is flammable; molten metal reacts violently with water). Furthermore, the traditional cover gas, SF₆, is a potent greenhouse gas, driving the industry to seek more environmentally friendly alternatives.
7. Applications & Cost
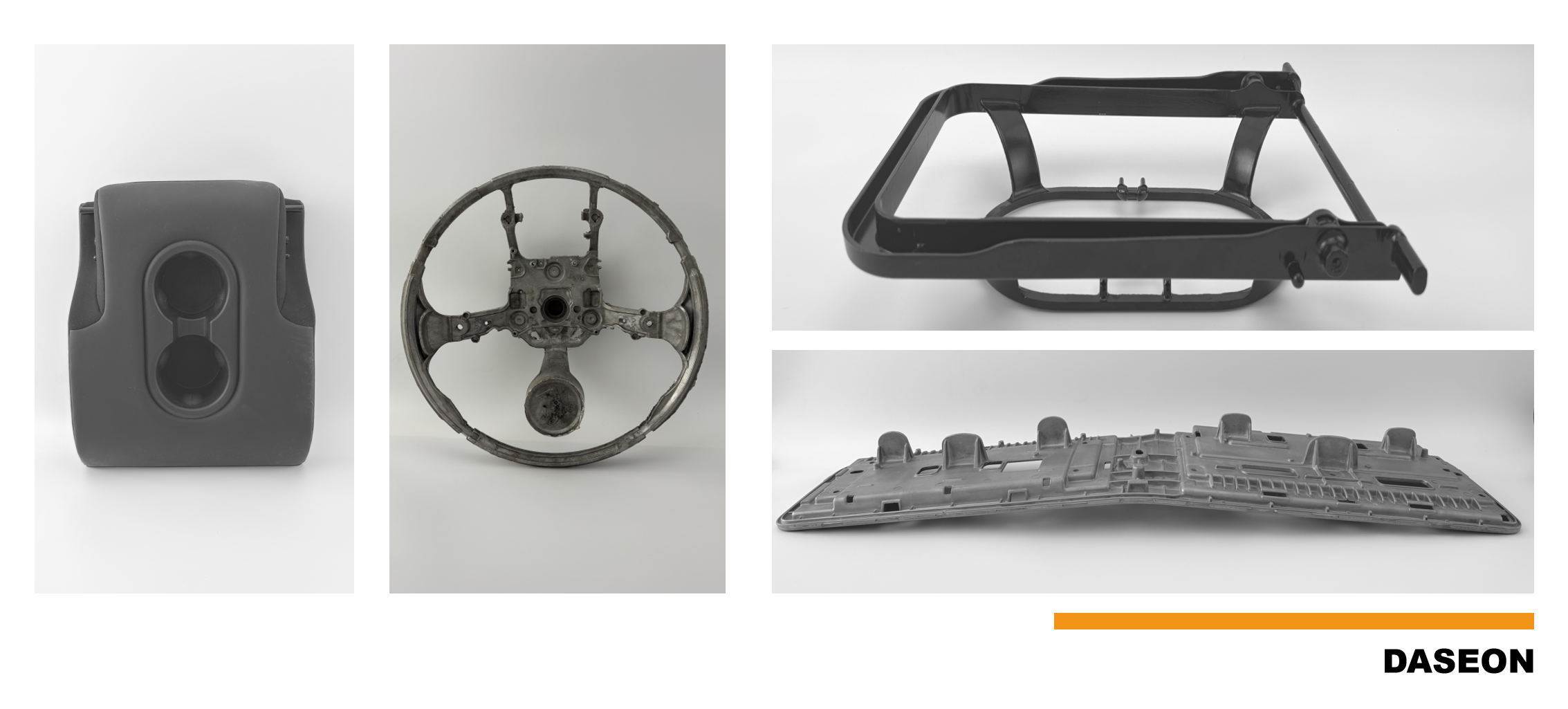
With its extreme light weight, excellent EMI shielding, and vibration damping properties, magnesium is widely used in 3C electronics, automotive steering wheels, and instrument panels. Aluminum, known for its mature process, excellent all-around properties, and cost-effectiveness, dominates in applications like automotive structural parts and engine blocks.
Our Professional Perspective
A deep understanding and command of these differences are prerequisites for achieving high-quality, high-efficiency die casting production. At DASEON, we not only provide industry-leading hot-chamber and cold-chamber die casting machines, but our comprehensive product matrix also includes gravity casting, low-pressure casting machines, and even cutting-edge magnesium semi-solid molding machines. Our expertise and complete range of equipment solutions ensure that no matter which material our clients choose, they are matched with the optimal production process to gain a competitive edge in the market.




